Nitrate-Free Interval Calculator
Maintain Effective Angina Treatment
This calculator helps determine when to take your next dose of isosorbide mononitrate to ensure the required 8-10 hour nitrate-free interval for optimal efficacy.
Why this interval matters: Regular use of nitrates without a nitrate-free period can lead to tolerance, reducing effectiveness. FDA guidelines recommend at least 8-10 hours without nitrate exposure daily to maintain efficacy.
Next Dose Time
No calculation yet
Your dosing schedule should include an 8-10 hour nitrate-free interval each day.
When it comes to treating chronic angina, Isosorbide mononitrate is a long‑acting nitrate medication that helps relax blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart muscle. It was first introduced in the United States in the early 1990s and has since become a staple in cardiovascular therapy. Understanding its FDA approval path and the current regulatory landscape is essential for clinicians, pharmacists, and patients alike.
Key Takeaways
- Isosorbide mononitrate received its first FDA approval in 1994 for the prevention of angina pectoris.
- The drug is classified as a prescription medication (ScheduleIII) under the Controlled Substances Act.
- Labeling must include nitrate‑specific warnings, contraindications, and a REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) for certain high‑dose formulations.
- Generic versions entered the market in 2003 after successful ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application) filings that demonstrated bioequivalence.
- Regulatory requirements differ in the EU, where the EMA approved the same molecule under the trade name Imdur in 1995.
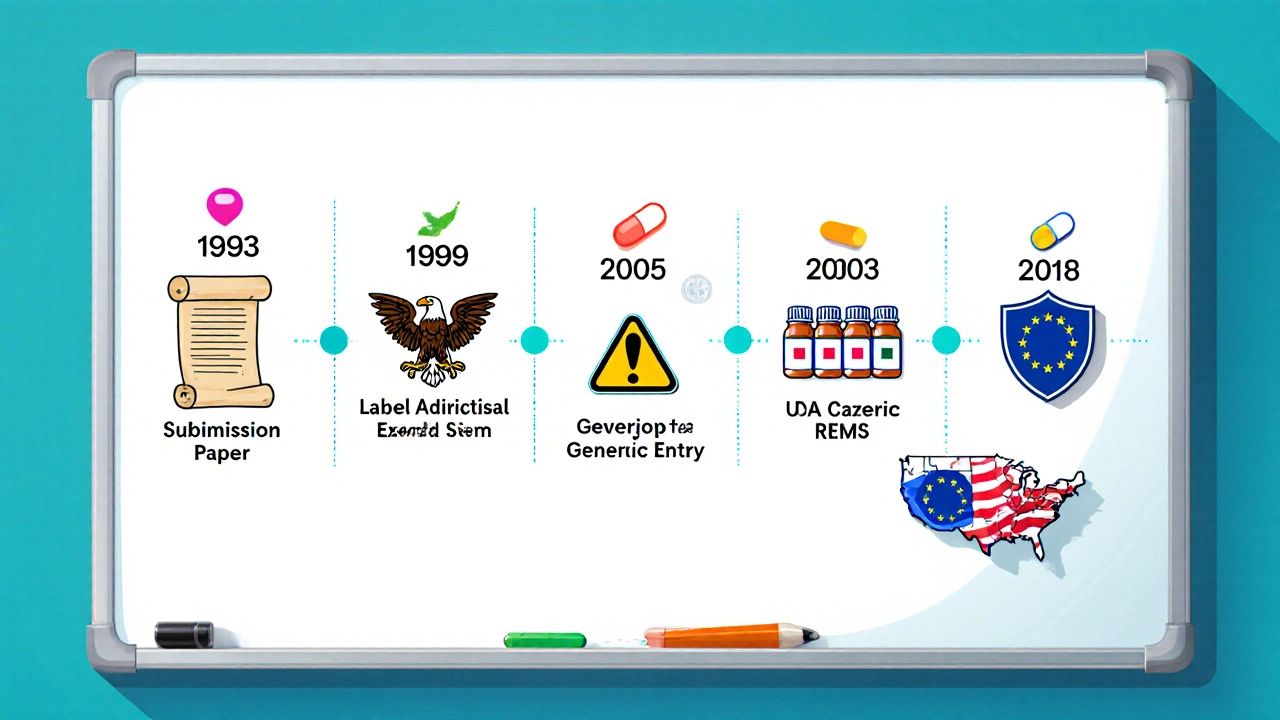
FDA Approval Timeline
The FDA’s review process for isosorbide mononitrate followed the standard New Drug Application (NDA) route. Below is a concise timeline:
- 1992: Sponsor submitted NDA to the FDA, including pharmacokinetic data, clinical efficacy in stable angina, and safety profiles.
- June 1994: FDA issued an approval letter, granting marketing rights for the extended‑release tablet (30mg and 60mg) and the immediate‑release tablet (5mg, 10mg, 20mg).
- 1999: FDA required a label revision to add a warning about severe hypotension when combined with PDE‑5 inhibitors.
- 2003: First generic ANDA approvals were granted after the patent for the brand‑name product (Imdur) expired.
- 2018: A REMS was introduced for the 120mg extended‑release formulation, aimed at minimizing misuse in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
These milestones illustrate how the FDA monitors both efficacy and safety throughout a drug’s lifecycle.
Regulatory Classification and Scheduling
Isosorbide mononitrate is not a controlled substance in the sense of narcotics, but under the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) it is listed as a prescription‑only medication, falling under ScheduleIII for certain high‑dose forms. This classification means:
- Physicians must write a valid prescription for any strength.
- Pharmacies can dispense up to a 30‑day supply without a refill request.
- Refills are limited to five per prescription, after which a new prescription is required.
Because nitrates can cause tolerance, the FDA’s labeling also recommends a “nitrate‑free interval” of at least 8-10hours daily to preserve efficacy.
Labeling, Safety Requirements, and REMS
The FDA’s labeling rules are driven by the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) standards for dosage forms and by specific safety concerns:
- Contraindications: Concurrent use with phosphodiesterase‑5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil) due to the risk of profound hypotension.
- Black‑box warning: Not required, but a prominent boxed warning highlights the risk of severe hypotension in patients with volume depletion.
- Pregnancy: CategoryC - benefits must outweigh potential risks.
- REMS: Implemented for the 120mg extended‑release tablet to ensure prescribers assess hepatic function before dispensing.
Pharmacists must counsel patients on proper storage (room temperature, protected from moisture) and on the importance of reporting dizziness or fainting episodes.
Generic Pathway, ANDA Success, and Bioequivalence
After the brand‑name patent expired, several manufacturers filed ANDAs. The FDA requires that each generic demonstrate:
- Pharmaceutical equivalence - the same active ingredient, dosage form, and strength.
- Bioequivalence - the 90‑percent confidence interval for the ratio of the generic to the reference product’s Cmax and AUC must fall between 80% and 125%.
Because isosorbide mononitrate has a relatively straightforward absorption profile, most generic products met the criteria on the first attempt. This resulted in a price drop of roughly 60% compared with the brand name, improving accessibility for patients with chronic angina.
International Comparison: FDA vs. EMA Regulations
| Aspect | FDA (United States) | EMA (European Union) |
|---|---|---|
| Approval route | NDA - full clinical data package required | MA - Mutual Recognition Procedure using existing EU data |
| First approval year | 1994 | 1995 |
| Prescription status | Prescription‑only (ScheduleIII for high‑dose) | Prescription‑only (no schedule) |
| Labeling warnings | Contraindication with PDE‑5 inhibitors, nitrate‑free interval | Same clinical warnings, plus EU‑specific contraindications for pregnant women |
| Generic pathway | ANDA with bioequivalence | Hybrid application - either full IND or bioequivalence dossier |
| Post‑marketing surveillance | FAERS reporting, REMS for high‑dose forms | EudraVigilance, risk management plan (RMP) |
Both agencies emphasize nitrate‑specific safety but differ in how they handle post‑marketing risk management. The EMA’s RMP is less prescriptive than the FDA’s REMS, reflecting regional regulatory philosophies.
Practical Guidance for Clinicians and Patients
Whether you’re prescribing, dispensing, or taking isosorbide mononitrate, keep these practical steps in mind:
- Check hepatic function before initiating the 120mg extended‑release product.
- Advise patients to avoid taking the drug within 24hours of any PDE‑5 inhibitor.
- Schedule a nitrate‑free interval each day to reduce tolerance.
- When switching to a generic, confirm that the pharmacy has performed a bioequivalence assessment.
- Monitor blood pressure regularly during the first two weeks of therapy, especially if the patient is on diuretics.
Following these steps aligns with FDA expectations and helps prevent adverse events.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is isosorbide mononitrate available over the counter in the US?
No. The FDA classifies it as a prescription‑only medication, so you need a valid doctor's prescription to obtain it.
What are the most common side effects?
Headache, dizziness, flushing, and low blood pressure are the typical adverse reactions. If they become severe, contact a health professional.
Can I take isosorbide mononitrate with nitroglycerin?
Yes, but the combined effect can increase the risk of hypotension. Physicians usually adjust dosages and schedule a nitrate‑free period.
When did generic versions become available?
The first generic ANDAs were approved in 2003, after the brand‑name patent expired. Multiple manufacturers now market equivalent tablets.
Is a REMS required for all strengths?
Only the 120mg extended‑release tablet carries a REMS. Lower‑strength tablets are exempt because the safety risk is lower.
How does the FDA define bioequivalence for this drug?
Bioequivalence means the generic’s Cmax and AUC values fall within 80‑125% of the reference product’s values, with a 90% confidence interval.
Are there any special storage requirements?
Store tablets at room temperature, away from excess heat and moisture. Do not refrigerate.





There are 18 Comments
Elijah Mbachu
Grate summary, thx for the info!
Sunil Rawat
Nice write up! It helps folks understand the FDA steps, especially the nitrate free interval part.
Sarah Hoppes
They dont want you to know the real risks behind nitrates they hide data
Erin Smith
Loving the clear steps this post gives it really helps patients stay safe and feel hopeful
George Kent
Excellent breakdown!!! Very thorough, well‑structured, and spot‑on regarding REMS!!! 👍👍👍
Jessica Davies
While this overview sounds comprehensive, it glosses over the nuanced pharmacodynamics that truly matter in clinical practice, which is a disservice to the informed reader.
Kyle Rhines
The FDA narrative is meticulously crafted; any deviation from the prescribed label is likely suppressed to protect corporate interests.
Lin Zhao
Great info! 😊 It’s good to see both US and EU perspectives side by side.
Albert Gesierich
Just to add, the 80‑125% bioequivalence range is standard for all NDAs, not a unique quirk of isosorbide mononitrate.
Suraj Midya
Regulatory differences matter; assuming US standards apply everywhere is a mistake.
ashish ghone
I'm glad you found the summary helpful! Remember to always schedule that nitrate‑free interval; patients often overlook it and end up with tolerance, which can be frustrating. Also, checking liver function before high‑dose forms is crucial, especially in older adults. Keep sharing these insights with your peers – education is the best tool we have 😊
steph carr
Absolutely, the practical tips on monitoring blood pressure are essential. It’s also wise to counsel patients about the interaction with PDE‑5 inhibitors to avoid dangerous hypotension.
Vera Barnwell
Wow, this article really dives deep into the regulatory maze of isosorbide mononitrate, and I have to say, it's impressive how detailed it gets. The historical timeline from 1992 to 2018 reads like a thriller, each year unveiling a new twist in the saga. I love that the author highlighted the REMS requirement for the 120 mg extended‑release form – that’s a critical safety net. Yet, I can’t shake the feeling that there’s an undercurrent of corporate influence shaping those guidelines. Have you noticed how the FDA warnings about PDE‑5 inhibitors appear just after the patent expiration? It feels almost like a strategic move to keep the market guarded. The comparison with the EMA is spot on, showcasing the subtle regulatory philosophy differences between the US and Europe. Speaking of philosophy, the table format is crystal clear, making the data instantly digestible. The practical steps for clinicians are gold, especially the liver function check before high‑dose prescriptions. I also appreciate the emphasis on patient education about nitrate‑free intervals – that’s often missed in primary care. However, the article could have expanded on the real‑world adherence challenges patients face. In my experience, many patients forget the interval and develop tolerance faster than anticipated. Also, the mention of generic bioequivalence could use a deeper dive into the 90 % confidence interval statistics. Overall, kudos for a comprehensive piece that balances technical detail with user‑friendly guidance. Keep up the great work, and maybe consider a follow‑up on post‑marketing surveillance data in the next update.
David Ross
Excellent analysis!!! The points about adherence challenges and statistical nuances are especially valuable!!! 👍
Henry Seaton
We need to watch the dosage schedule carefully
Baby Thingie
The bioequivalence range is indeed 80‑125% with a 90% confidence interval. 😊
Abby Elizabeth
Ugh, another over‑the‑top praise, it feels like an echo chamber of blind admiration!!! 🙄
Mark Haycox
Your conspiracy ramblings ignore the robust FDA data; it’s misleading and undermines patient safety.
Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *